China’s Exports are Slipping due to Several Challenges in 2020

After joining the World Trade Organization in 2008, China has become the world’s factory, foreign trade has developed rapidly, and the annual export growth is on average 1.5 times that of GDP, and foreign trade has become the fastest in the “troika”.
Chinese export, as one of the troikas in driving economic growth, is severe and not promising in 2020. The data confirms this statement. Although exports of anti-epidemic supplies have grown vigorously, China’s foreign trade data in May is still dragged down by a variety of factors. Exports have changed from rising to falling.
Cost-Effective Agency
KPI and Results focused. We are the most visible Marketing Agency for China. Not because of huge spending but because of our SMART Strategies. Let us help you with: E-Commerce, Search Engine Optimization, Advertising, Weibo, WeChat, WeChat Store & PR.
The growth of China’s exports in the international market is experiencing a downwards slopping trend. With multiple difficulties, China’s foreign trade is facing a similar but more difficult situation than after the 2008 financial crisis.
What are the reasons for this decline?
In 2006, exports of goods and services accounted for a peak of 36% of GDP. However, the advent of the financial crisis caused this data to plummet to 24.5% in 2009. China was forced to shift the pillar of the economy to the other two drivers – investment and consumption.
In 2018, the share of exports in GDP has stabilized at around 19%, and export is no longer the main driving force of China’s economy. The reasons for these falling export figures are complex. Several factors have contributed to this decline:
- Chinese currency (yuan) appreciation;
- Poor demand in the international market;
- Relocation;
- The difficult structural transformation of the Chinese economy.
Chinese currency (yuan) appreciation
Since 2017, the RMB exchange rate has appreciated by more than 10%, and the spot exchange rate has exceeded 6.28. Especially in 2018, the RMB appreciation momentum has been rapid, far exceeding market expectations.
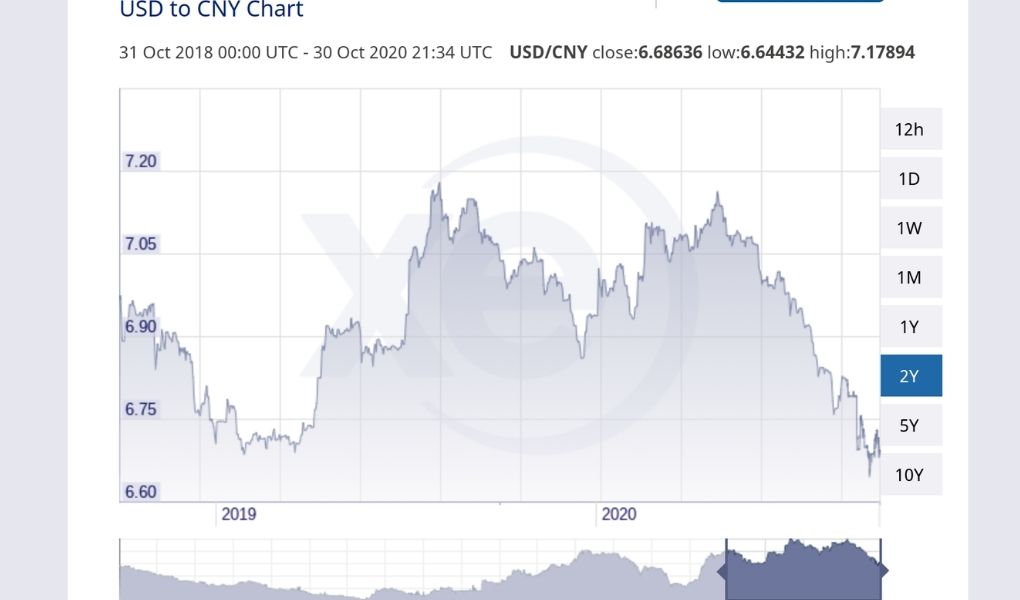
According to data from XE, since May, the yuan has been appreciating. On September 16, the central parity of the RMB exchange rate in the inter-bank foreign exchange market was 1 U.S. dollar to RMB 6.7825, a sharp increase of 397 basis points from the previous trading day, breaking the 6.8 mark. Early in May, it was 7.1316, in just three months, the central parity of the RMB against the US dollar appreciated by 3,491 basis points and reached a record high of 6.69 since April 2019.
Three reasons for this appreciation of yuan:
- China’s economic recovery – main reason;
- U.S. dollar index continues to fall, and non-US currencies including the renminbi have seen an appreciation trend;
- International investors are optimistic about China’s economic prospects and renminbi assets, thus foreign capital inflows are continuously injected into China’s capital market.
From the perspective of exports, the appreciation of the Chinese currency will give exporting trade pressure and lower export profits. The more orders come in, the more fear of selling at a loss.
External demand in China is witnessing a downturn
The biggest impact on China’s foreign trade is still the weakness of external demand. Many countries in Europe and the United States where the epidemic is raging have maintained deficits with China. Large-scale blockade measures have basically suspended commercial activities and canceled a large number of foreign trade orders.
The new round of restrictive measures due to the second wave of the pandemic will continue to weaken consumer demand in these countries, which will have an adverse effect on China’s exports in the short term.
China is also facing Relocation
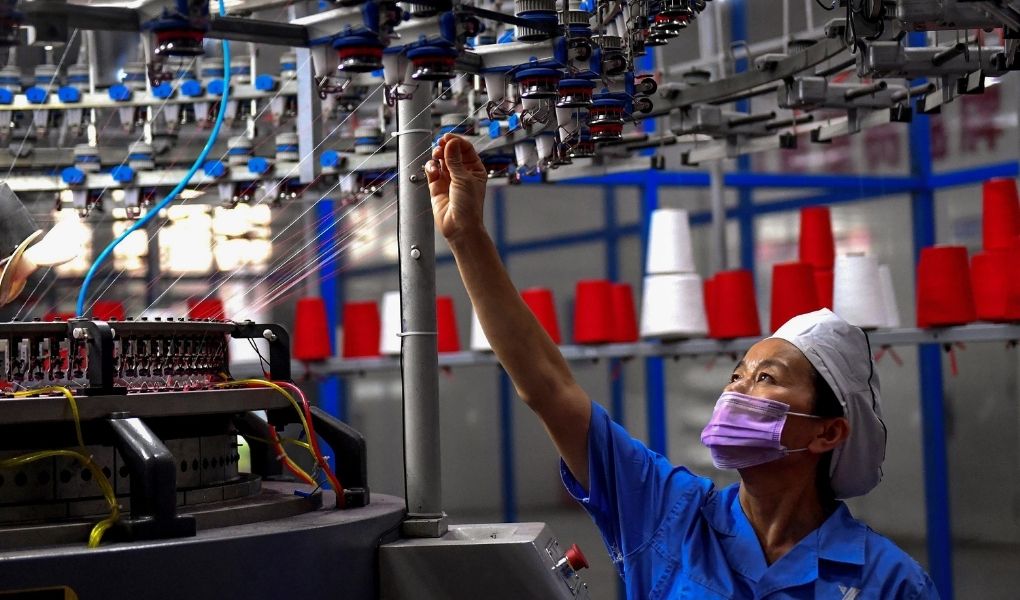

During the past years, the cost of labor and raw materials has rapidly increased in China. Raw material costs have increased by 10 to 20%, and labor costs have increased by 30%. This increase in costs has led to the relocation of plants to other emerging Asian countries where the labor and material costs are lower than China, for example, India, Vietnam.
Indian textile, as the cell phone manufacturing industry, are both looking outward, especially to India. Aiming to attract foreign investment, the Indian government launched a $6.6 billion incentive program and a $1.4 trillion infrastructure plan to make India a new manufacturing center for smartphones.
The giant phone manufacturer – Apple has already relocated six production lines from China to India and is planning to move more to India.
China is losing its advantages as the factory of the world and this can not be changed. Therefore, it gropes towards the transformation to find other ways to maintain its economic growth.
The difficult structural transformation of the Chinese economy
According to data from Statista, China’s GDP results were down to 4.9% in the third quarter and 0.7% in the first three quarters. Among the three main components of GDP, export is still the main driver of economic growth, while consumption lagged behind investment and exports.
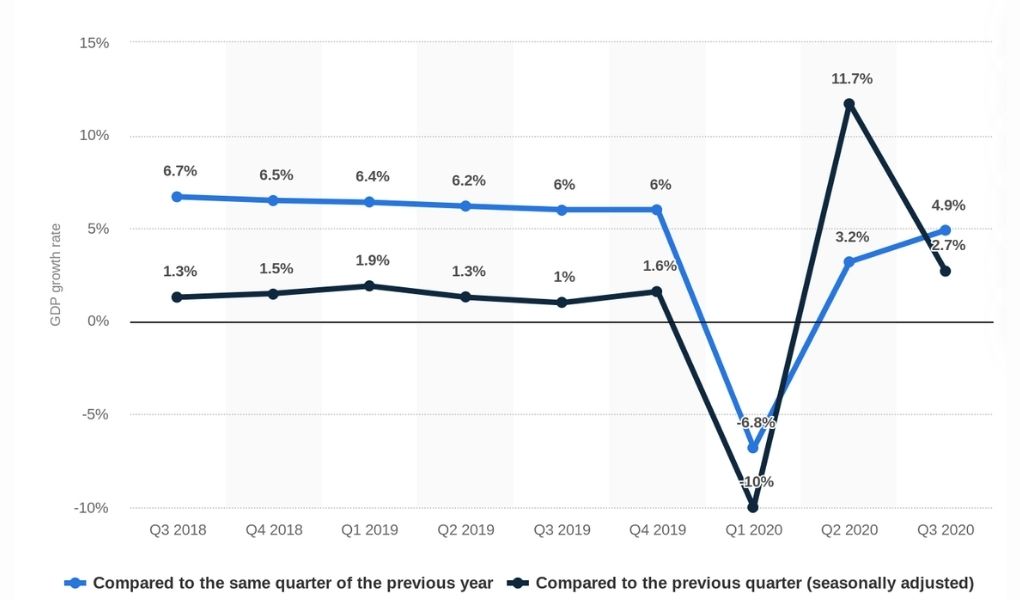
The Chinese economy is highly independent of real estate and this can not be changed in a short time although many measures have been taken. Suffering from the “property bubble”, China insists on not using real estate as a short-term economic stimulus.
The real estate market once played a huge role in stimulating the rapid growth of China’s economy, so without the huge “accelerator” of real estate, what other “accelerators” can be used to stimulate China’s economic recovery in the future?
- Repair the industrial chain and supply chain;
- Create more employment opportunities (a prerequisite for stable consumption);
- Deepen reforms to create a higher-level business environment and activate the motivation and vitality of market players;
- Promote innovation and technology.
USA/China: Deteriorating Trade Environment

The deterioration of relations between the United States and China has reinforced American and European companies’ concerns about their excessive dependence on China and has further worsened the problems.
The poor bilateral relations with India and Australia hinder China’s foreign trades. As far as China’s export is concerned, this deterioration has made China’s situation worse. India’s annual trade with China exceeds 88 billion U.S. dollars, with a deficit of more than 53 billion U.S. dollars. China is the country with the largest deficit in India.
Since 2018, the trade war between China and the U.S. has caused a loss on both sides. In the field of science and technology, the United States has initiated several restrictive measures against China. The U.S. announced on May 15 that manufacturers must obtain an export license from the U.S. government when exporting semiconductor chips that use U.S. technology or designs to Huawei, even for manufacturers outside the U.S.
Moreover, the United States has recently actively lobbied its allies to ban Huawei’s 5G equipment, causing the company to retreat in many European and American markets. Cracking down on them will directly put pressure on China’s exports. In addition, it will also affect China’s economic transformation to high-end manufacturing.

GMA is not only a Chinese market analyst but also a Chinese digital marketing expert. If you have any questions about China or how to enter the Chinese market, feel free to contact us.
Our services include:
- Advertising in China
- Baidu SEO/SEM
- Social media agency
- PR
- KOL marketing
- many others






